Visual Follow Line
Goal
The goal of this exercise is to implement a PID reactive control capable of following the line painted on the racing circuit.



The students will program a Formula1 car in a race circuit to follow the red line in the middle of the road.
Frequency API
Python
import Frequency- to import the Frequency library class. This class contains the tick function to regulate the execution rate.Frequency.tick(ideal_rate)- regulates the execution rate to the number of Hz specified. Defaults to 50 Hz.
C++
#include "Frequency.hpp"- to import the Frequency library class. This class contains the tick function to regulate the execution rate.Frequency freq = Frequency();- to instanciate the Frequency class.freq.tick(ideal_rate);- regulates the execution rate to the number of Hz specified. Defaults to 50 Hz.
Robot API
This exercise now supports ROS 2-native implementation in addition to the original HAL-based approach. Below you’ll find the details for both options.
HAL-based Implementation
Python
import HAL- to import the HAL (Hardware Abstraction Layer) library class. This class contains the functions that send and receive information to and from the Hardware (Gazebo).import WebGUI- to import the WebGUI (Web Graphical User Interface) library class. This class contains the functions used to view the debugging information, like image widgets.HAL.getImage()- to get the image (BGR8).HAL.setV(velocity)- to set the linear speed.HAL.setW(velocity)- to set the angular velocity.WebGUI.showImage(image)- allows you to view a debug image or with relevant information.
C++
#include "HAL.hpp"- to import the HAL (Hardware Abstraction Layer) library class. This class contains the functions that send and receive information to and from the Hardware (Gazebo).#include "WebGUI.hpp"- to import the WebGUI (Web Graphical User Interface) library class. This class contains the functions used to view the debugging information, like image widgets.HAL::get_image();- to get the image (cv::Mat).HAL::set_v(velocity);- to set the linear speed.HAL::set_w(velocity);- to set the angular velocity.WebGUI::show_image(image);- allows you to view a debug image (cv::Mat) or with relevant information.
ROS 2-native Implementation
ROS 2 Topics
Use standard ROS 2 topics for direct communication with the simulation.
/cam_f1_left/image_raw- Subscribe to this topic to receive camera images (BGR8). Message type:sensor_msgs/msg/Image/cmd_vel- Publish to this topic to set both linear and angular velocities. Message type:geometry_msgs/msg/Twist
For image debugging:
/webgui_image- Publish to this topic to set the debug image in the GUI interface. Message type:sensor_msgs/msg/Image
Python
Note: Ensure this import is included in your script to access the Web GUI functionalities.
from WebGUI import gui - to enable the Web GUI for visualizing camera images.
To have frequency control you need to use standard ROS 2 mechanisms to manage loop timing:
rclpy.spin()- Event-driven execution using callbacks.rclpy.spin_once()- Single-step processing, often with custom timers.rclpy.Rate()- Loop-based frequency control.
C++
In order to use native ros controls you must include the following lines:
#ifndef USER_NODE
#define USER_NODE
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
class UserNode : public rclcpp::Node {
// Your class
};
#endif
You must define USER_NODE and a UserNode node class.
To have frequency control you may use a timer and a control function as follows:
UserNode() : Node("user_node")
{
// More subscribers and publishers
timer_ = create_wall_timer(100ms, std::bind(&UserNode::control_cycle, this));
};
// More Code
void control_cycle(){
// Your function
};
Theory
PID Control is the foundation of the implementation for this exercise. To understand PID Control, let us first understand what is Control in general.
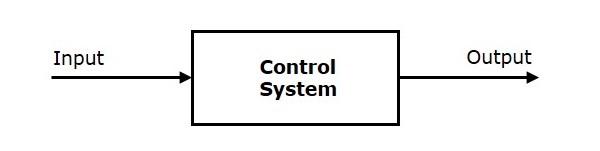
Control System
A system or set of devices, that manages, commands, directs or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems to achieve the desired results. Simply speaking, a system which controls other systems. Control Systems help a robot execute a set of commands precisely, in the presence of unforeseen errors or complications.
Types of Control System
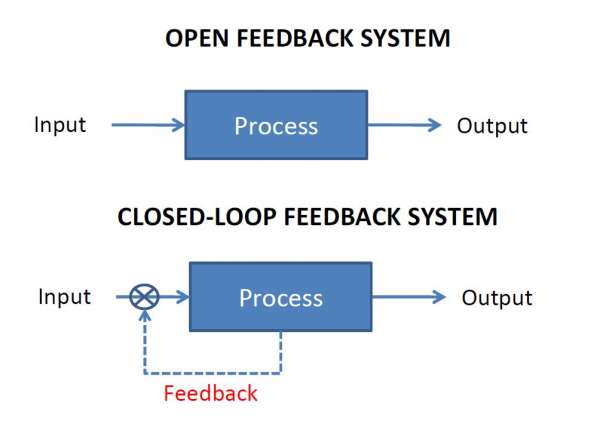
Open Loop Control System
A control system in which the control action is completely independent of the output of the system. An Open Loop System is a manual control system.
Closed Loop Control System
A control system in which the output has an effect on the input quantity in such a manner that the input will adjust itself based on the output generated. An open loop system can be converted to a closed one by providing feedback.
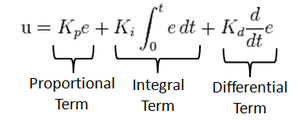
PID Control
A control loop mechanism using feedback. A PID Controller continuously calculates an error value as the difference between the desired output and the current output and applies a correction based on proportional, integral and derivative terms(denoted by P, I, D respectively).
- Proportional
A Proportional Controller gives an output which is proportional to the current error. The error is multiplied with a proportionality constant to get the output. And hence, is 0 if the error is 0.
- Integral
An Integral Controller provides a necessary action to eliminate the offset error which is accumulated by the P Controller. It integrates the error over a period of time until the error value reaches zero.
- Derivative
A Derivative Controller gives an output depending on the rate of change or error regarding time. It gives the kick start for the output thereby increasing system response.
Tuning Methods
In order for the PID equation to work, we need to determine the constants of the equation. There are 3 constants called the gains of the equation. We have 2 major tuning methods for this.
- Trial and Error
It is a simple method of PID controller tuning. While the system or controller is working, we can tune the controller. In this method, first we have to set Ki and Kd values to zero and increase proportional term (Kp) until system reaches oscillating behavior. Once it is oscillating, we adjust Ki (Integral term) so that oscillations stops and finally adjust D to get a fast response.
- Zeigler-Nichols method
Zeigler-Nichols proposed closed loop methods for tuning the PID controller. Those are: continuous cycling method and damped oscillation method. The procedures for both methods are the same but their oscillation is different. Therefore, first we have to set the p-controller constant, Kp to a particular value while Ki and Kd values are zero. Proportional gain is increased until the system oscillates at a constant amplitude.
Real Life Example
Hints
Simple hints provided to help you solve the follow_line exercise.
References to ROS 2 Concepts
Understanding these ROS 2 concepts will help you implement the exercise natively. Refer to these links for more details:
- ROS 2 Publisher & Subscriber – https://docs.ros.org/en/humble/Tutorials/Beginner-Client-Libraries/Writing-A-Simple-Py-Publisher-And-Subscriber.html
- ROS 2 Spin & Spin Once – https://docs.ros.org/en/rolling/p/rclpy/api/init_shutdown.html
Detecting the Line to Follow
The first task of the assignment is to detect the line to be followed. This can be achieved easily by filtering the color of the line from the image and applying basic image processing to find the point or line to follow, or in Control terms our Set Point. Refer to these links for more information:
- https://www.pyimagesearch.com/2014/08/04/opencv-python-color-detection/
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/10469235/opencv-apply-mask-to-a-color-image
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/22470902/understanding-moments-function-in-opencv
Coding the Controller
The Controller can be designed with various configurations. 3 configurations have been described in detail below:
-
P Controller The simplest way to do the assignment is using the P Controller. Just find the error which is the difference between our Set Point (The point where our car should be heading) and the Current Output (Where the car is actually heading). Keep adjusting the value of the constant, until we get a value where there occurs no unstable oscillations and no slow response.
-
PD Controller This is an interesting way to see the effect of the derivative on the Control. For this, we need to calculate the derivative of the output we are receiving. Since, we are dealing with discrete outputs in our case, we simply calculate the difference between our previous error and the present error, then adjust the proportional constant. Adjust this value along with the P gain to get a good result.
-
PID Controller This is the completely implemented controller. Now, to add the I Controller we need to integrate the output from the point where error was zero, into the present output. While dealing with discrete outputs, we can achieve this using accumulated error. Then, comes the task of adjustment of gain constants until we get our desired result.
Illustrations


Videos
This solution is an illustration for the Web Templates
Demonstrative video of the solution
Contributors
- Contributors: Alberto Martín, Francisco Rivas, Francisco Pérez, Jose María Cañas, Nacho Arranz, Javier Izquierdo, Ashish Ramesh.
- Maintained by Javier Izquierdo.
References
- https://www.electrical4u.com/control-system-closed-loop-open-loop-control-system/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PID_controller
- https://www.elprocus.com/the-working-of-a-pid-controller/
- https://www.tutorialspoint.com/control_systems/control_systems_introduction.htm
- https://instrumentationtools.com/open-loop-and-closed-animation-loop/
- https://trinirobotics.com/2019/03/26/arduino-uno-robotics-part-2-pid-control/
- http://homepages.math.uic.edu/~kauffman/DCalc.pdf