Autoparking
Objective
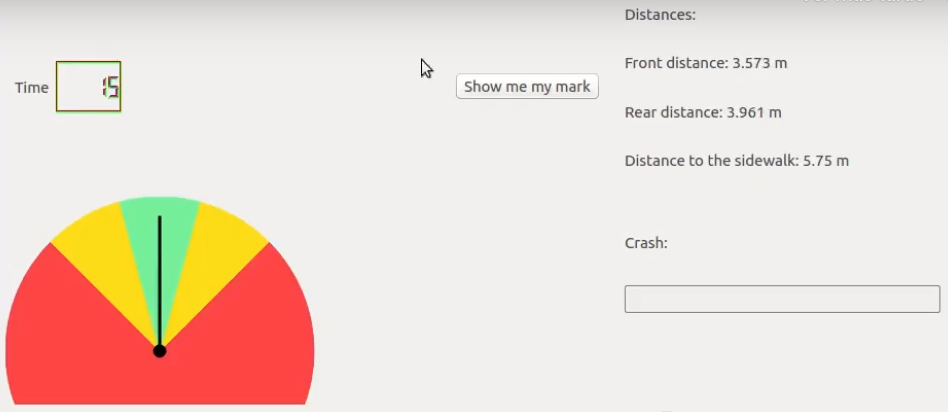
The objective of this practice is to implement the logic of a navigation algorithm for an automated vehicle. The vehicle must find a parking space and park properly.
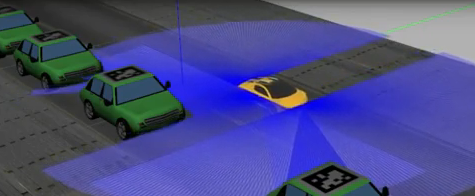
Instructions
Installing and Launching
-
Download Docker. Windows users should choose WSL 2 backend Docker installation if possible, as it has better performance than Hyper-V.
-
Pull the current distribution of Robotics Academy Docker Image:
docker pull jderobot/robotics-academy:latest
-
In order to obtain optimal performance, Docker should be using multiple CPU cores. In case of Docker for Mac or Docker for Windows, the VM should be assigned a greater number of cores.
-
It is recommended to use the latest image. However, older distributions of RADI (Robotics-Academy Docker Image) can be found here.
How to perform the exercises?
-
Start a new docker container of the image and keep it running in the background:
docker run --rm -it -p 7164:7164 -p 2303:2303 -p 1905:1905 -p 8765:8765 -p 6080:6080 -p 1108:1108 -p 7163:7163 jderobot/robotics-academy -
On the local machine navigate to 127.0.0.1:7164/ in the browser and choose the desired exercise.
-
Wait for the Connect button to turn green and display “Connected”. Click on the “Launch” button and wait for some time until an alert appears with the message
Connection Establishedand button displays “Ready”. -
The exercise can be used after the alert.
Enable GPU Acceleration
- Follow the advanced launching instructions from here.
Where to insert the code?
In the launched webpage, type your code in the text editor,
from GUI import GUI
from HAL import HAL
# Enter sequential code!
while True:
# Enter iterative code!
Using the Interface
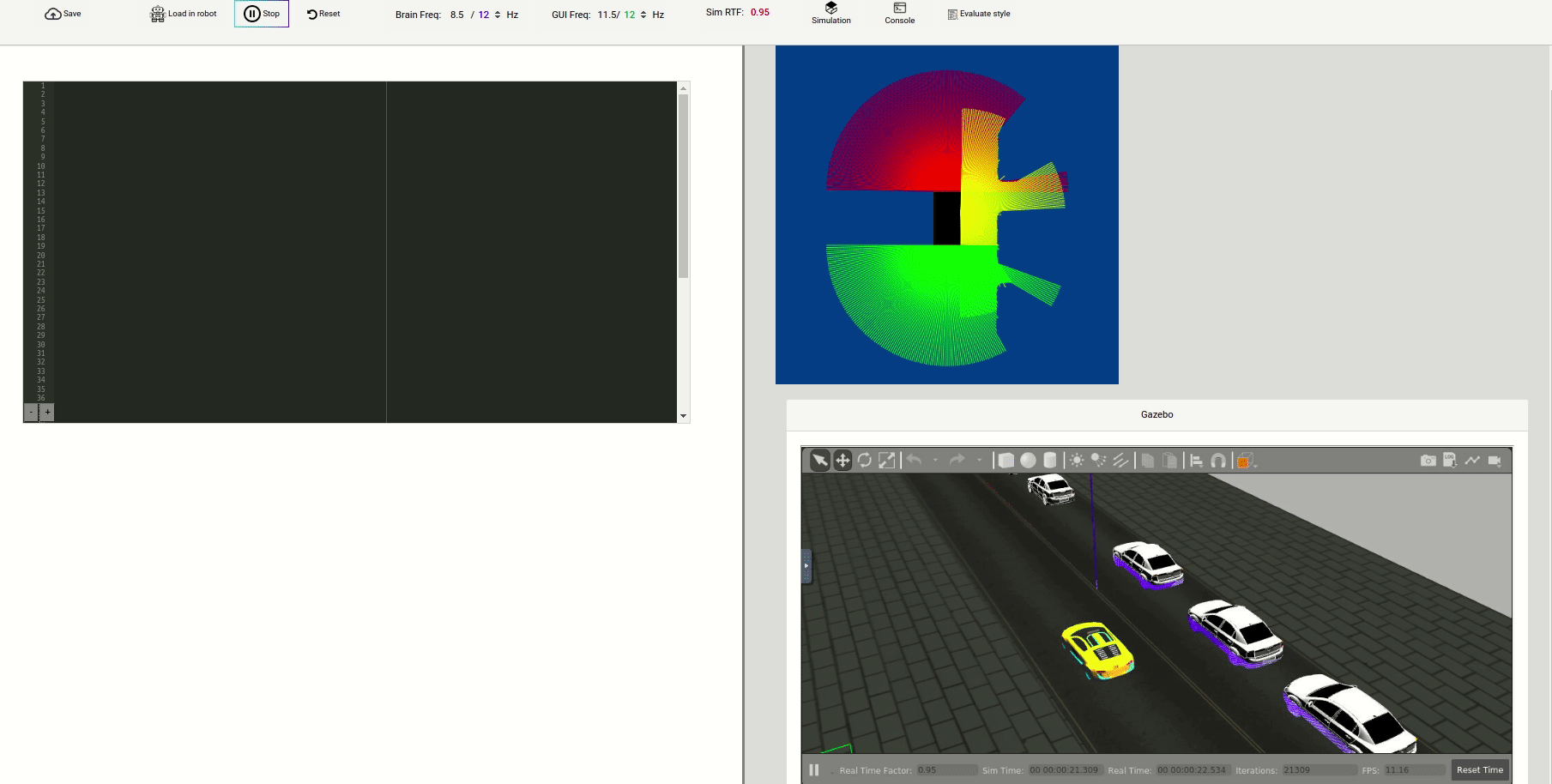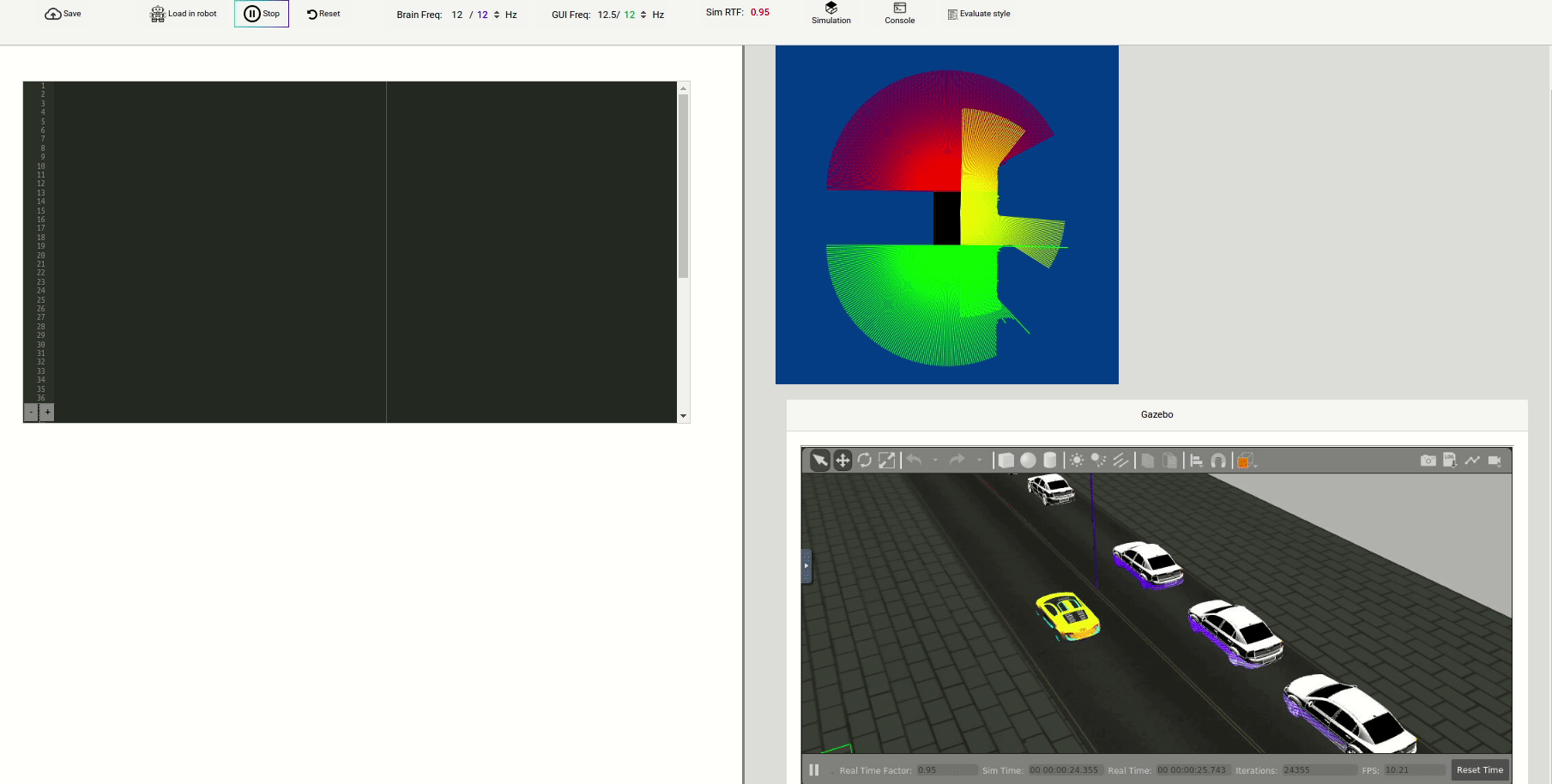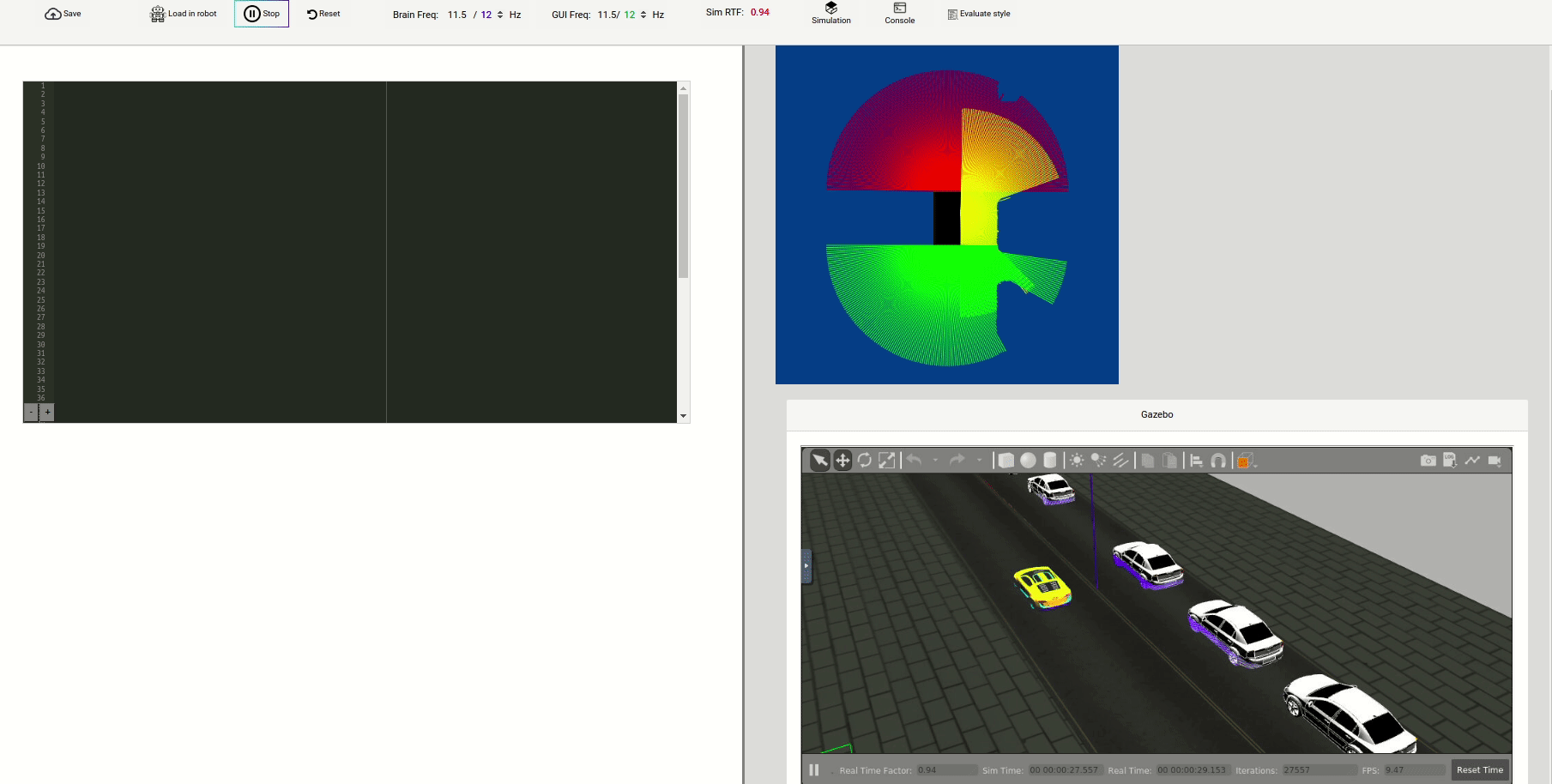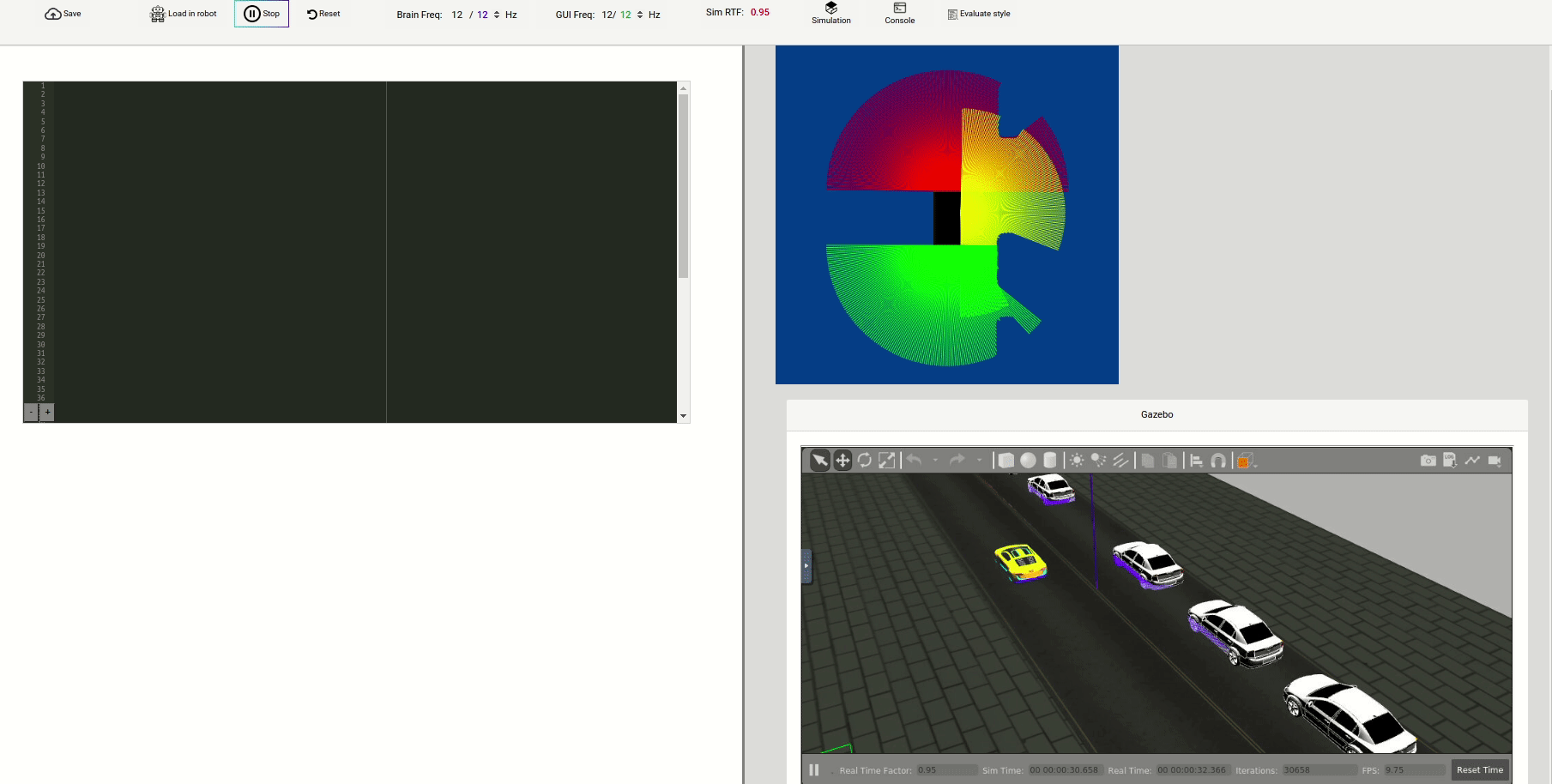
-
Control Buttons: The control buttons enable the control of the interface. Play button sends the code written by User to the Robot. Stop button stops the code that is currently running on the Robot. Save button saves the code on the local machine. Load button loads the code from the local machine. Reset button resets the simulation(primarily, the position of the robot).
-
Brain and GUI Frequency: This input shows the running frequency of the iterative part of the code (under the
while True:). A smaller value implies the code runs less number of times. A higher value implies the code runs a large number of times. The numerator is the one set as the Measured Frequency who is the one measured by the computer (a frequency of execution the computer is able to maintain despite the commanded one) and the input (denominator) is the Target Frequency which is the desired frequency by the student. The student should adjust the Target Frequency according to the Measured Frequency. -
RTF (Real Time Factor): The RTF defines how much real time passes with each step of simulation time. A RTF of 1 implies that simulation time is passing at the same speed as real time. The lower the value the slower the simulation will run, which will vary depending on the computer.
-
Console: This shows the error messages related to the student’s code that is sent. In order to print certain debugging information on this console, the student is provided with
print()command in the Python Interpreter. -
Simulation: This shows the Gazebo window allowing the student to visualize the 3D world and control its elements.
Robot API
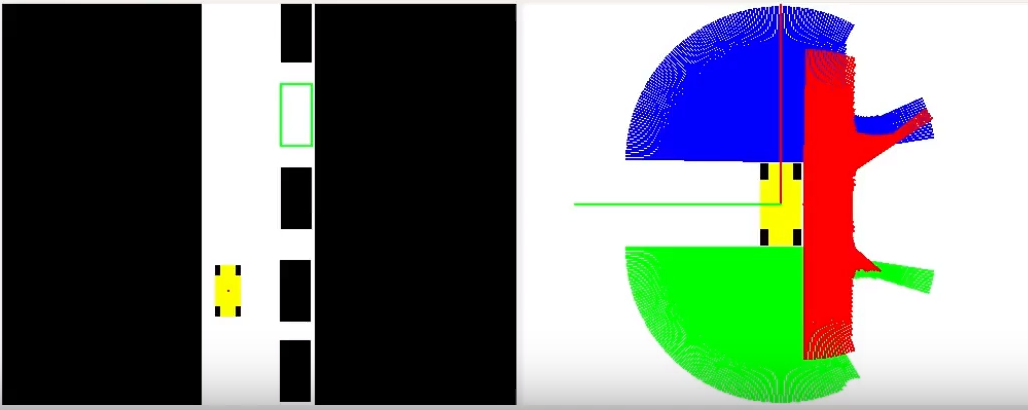
from HAL import HAL- to import the HAL(Hardware Abstraction Layer) library class. This class contains the functions that sends and receives information to and from the Hardware(Gazebo).from GUI import GUI- to import the GUI(Graphical User Interface) library class. This class contains the functions used to view the debugging information, like image widgets.HAL.getPose3d()- to get all the position informationHAL.getPose3d().x- to get the position of the robot (x coordinate)HAL.getPose3d().y- to get the position of the robot (y coordinate)HAL.getPose3d().yaw- to get the orientation of the robot with regarding the mapHAL.getFrontLaserData()- to obtain the front laser sensor data It is composed of 180 pairs of values: (0-180º distance in millimeters)HAL.getRightLaserData()- to obtain the right laser sensor data It is composed of 180 pairs of values: (0-180º distance in millimeters)HAL.getBackLaserData()- to obtain the back laser sensor data It is composed of 180 pairs of values: (0-180º distance in millimeters)HAL.setV()- to set the linear speedHAL.setW()- to set the angular velocity
Laser attributes
HAL.getFrontLaserData(), HAL.getRightLaserData() and HAL.getBackLaserData() returns an instance of a Class with the following attributes:
minAngle- Start angle of the scan [rad]maxAngle- End angle of the scan [rad]minRange- minimum range value [m]maxRange- maximum range value [m]values- A list of 180 measurements [m] (Note: values < minRange or > maxRange should be discarded)
Illustrations
Videos
Contributors
- Contributors: Vanessa Fernández Martínez
- Maintained by Vanessa Fernández Martínez