RoboticsAcademy with Visual Circuit
Goal
The goal of this exercise is to implement the logic that allows a quadrotor to follow a road. In order to do this, you will have to establish a color filter to segment road lines and then develop an algorithm to follow them until the end of the road.

Instructions for Running Follow Road on Noetic
This is the preferred way for running the exercise.
Installation
- The installation instructions can be found here.
How to perform the exercise?
- Run the follow road exercise by going to the following directory: “RoboticsAcademy/exercises/static/exercises/follow_road”
-
Run the following command to launch it:
roslaunch follow_road.launch
Theory
PID Control is the main fundamental behind this exercise. To understand PID Control, let us first understand what is Control in general.
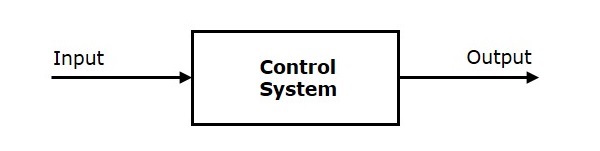
Control System
A system of devices or set of devices, that manages, commands, directs or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems to achieve the desired results. Simply speaking, a system which controls other systems. Control Systems help a robot to execute a set of commands precisely, in the presence of unforeseen errors.
Types of Control System
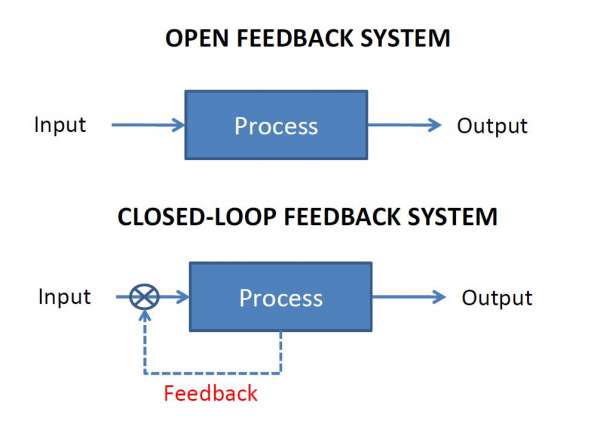
Open Loop Control System
A control system in which the control action is completely independent of the output of the system. A manual control system is on Open Loop System.
Closed Loop Control System
A control system in which the output has an effect on the input quantity in such a manner that the input will adjust itself based on the output generated. An open loop system can be converted to a closed one by providing feedback.
PID Control
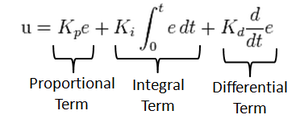
A control loop mechanism employing feedback. A PID Controller continuously calculates an error value as the difference between desired output and the current output and applies a correction based on proportional, integral and derivative terms(denoted by P, I, D respectively).
- Proportional
Proportional Controller gives an output which is proportional to the current error. The error is multiplied with a proportionality constant to get the output. And hence, is 0 if the error is 0.
- Integral
Integral Controller provides a necessary action to eliminate the offset error which is accumulated by the P Controller.It integrates the error over a period of time until the error value reaches to zero.
- Derivative
Derivative Controller gives an output depending upon the rate of change or error with respect to time. It gives the kick start for the output thereby increasing system response.
Tuning Methods
In order for the PID equation to work, we need to determine the constants of the equation. There are 3 constants called the gains of the equation. We have 2 main tuning methods for this.
- Trial and Error
It is a simple method of PID controller tuning. While system or controller is working, we can tune the controller. In this method, first we have to set Ki and Kd values to zero and increase proportional term (Kp) until system reaches to oscillating behavior. Once it is oscillating, adjust Ki (Integral term) so that oscillations stops and finally adjust D to get fast response.
- Zeigler Nichols method
Zeigler-Nichols proposed closed loop methods for tuning the PID controller. Those are continuous cycling method and damped oscillation method. Procedures for both methods are same but oscillation behavior is different. In this, first we have to set the p-controller constant, Kp to a particular value while Ki and Kd values are zero. Proportional gain is increased till system oscillates at constant amplitude.
Hints
Simple hints provided to help you solve the follow_road exercise. Please note that the full solution has not been provided.
Detecting the road to follow
The first task of the assignment is to detect the line to be followed. This can be achieved easily by filtering the color of the road from the image and applying basic image processing to find the point or line to follow.
Directional control. How should drone yaw be handled?
If you don’t take care of the drone yaw angle or yaw_rate in your code (keeping them always equal to zero), you will fly in what’s generally called Heads Free Mode. The drone will always face towards its initial orientation, and it will fly sideways or even backwards when commanded towards a target destination. Multi-rotors can easily do that, but what’s not the best way of flying a drone.
In this exercise, your drone should follow the path similarly to how a fixed-wing aircraft would do, namely nose forward. Then, you’ll have to implement by yourself some kind of directional control, to rotate the nose of your drone left or right using yaw angle, or yaw_rate.
Coding the Controller
The Controller can be designed in various configurations. 3 configurations have been described in detail below:
-
P Controller The simplest way to do the assignment is using the P Controller. Just find the error which is the difference between our Set Point (the point where our drone should be heading) and the Current Output (where the drone is actually heading). Keep adjusting the value of the constant, till we get a value where there occurs no unstable oscillations and no slow response.
-
PD Controller This is an interesting way to see the effect of Derivative on the Control. For this, we need to calculate the derivative of the output we are receiving. Since, we are dealing with discrete outputs in our case, we simply calculate the difference between our previous error and the present error, then adjust the proportional constant. Adjust this value along with the P gain to get a good result.
-
PID Controller This is the complete implemented controller. Now, to add the I Controller we need to integrate the output from the point where error was zero, to the present output. While dealing with discrete outputs, we can achieve this using accumulated error. Then, comes the task of adjustment of gain constants till we get our desired result.
Building the application using VisualCircuit
Blocks Used
CameraROS
ColorFilter
CustomCode
PID Controller
Motor Driver
Demonstrative video of the solution
Contributors
- Contributors: Nikhil Khedekar, JoseMaria Cañas, Diego Martín, Pedro Arias] and Prakarsh Kaushik.
- Maintained by Pedro Arias, Muhammad Taha and Prakarsh Kaushik.
