Beginner's Tutorial
Sample video depicting results of this tutorial:
Detection Metrics Supports lot’s of functionalities for both Datasets and Inferencers, some of them are viewing different datasets (Viewer), converting datasets from one to another (Converter), generating detection datasets (Detector), evaluating datasets using inferencers (Evaluator, Auto Evaluator) and finally deploying datasets(Deployer).
Detection Metrics has both GUI app and command line tools to execute its functionalities.
But as a beginner on should always start with GUI app, named DatasetEvaluationApp. We will start with Deployer Tab in the same app.
Once you’ve build DetectionMetrics (for building, refer here), navigate to DatasetEvaluationApp directory in the build directory using the following command from Detection Metrics’s root directory:
cd DetectionMetrics/build/DatasetEvaluationApp/
You will find an executable there, to run it you need:
- Config file
- Inferencer
Just create some directories using the following commands:
sudo mkdir /opt/datasets # Root directory containing all datasets and inferencers
sudo mkdir /opt/datasets/weights # Directory containing Inferencer weights
sudo mkdir /opt/datasets/cfg # Directory containing Config files for different inferencers
sudo mkdir /opt/datasets/names # Contains txt files listing classnames for various datasets
sudo mkdir /opt/datasets/output # Evaluations output
Also, give this directory read and write permissions, so that files can be read from and written to this directory:
sudo chmod -R 666 /opt/datasets
For this tutorial we will need inferencer weights, config files and a class names file, and can be downloaded as follow:
-
Inferencer weights and config files: Our model zoo. You can choose any model for various frameworks trained on different datasets. Note: TensorFlow and Keras doesn’t require any config files, just create an empty
foo.cfgfile in thecfgfolder. -
Datasets Class Names File: Can be Downloded from here .
For this tutorial, we will be using SSD MobileNet v1, trained on COCO, and would require following files:
- Model: ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco.
- Config: Just Create an empty foo.cfg file in
cfg/. - ClassNames: Download COCO ClassNames File.
Now, we will create a yaml config file, to be passed as a parameter in DatasetEvaluationApp.
Sample config file for above created directory structure.
datasetPath: /opt/datasets/
evaluationsPath: /opt/datasets/eval
weightsPath: /opt/datasets/weights
netCfgPath: /opt/datasets/cfg
namesPath: /opt/datasets/names
If you have created the directories as mentioned above, then just copy paste, above data into appConfig.yml, else make changes accordingly.
Now, we are good to go ![]()
![]() !!
!!
Just type ./DatasetEvaluationApp -c appConfig.yml
And you will see a GUI pop like this:
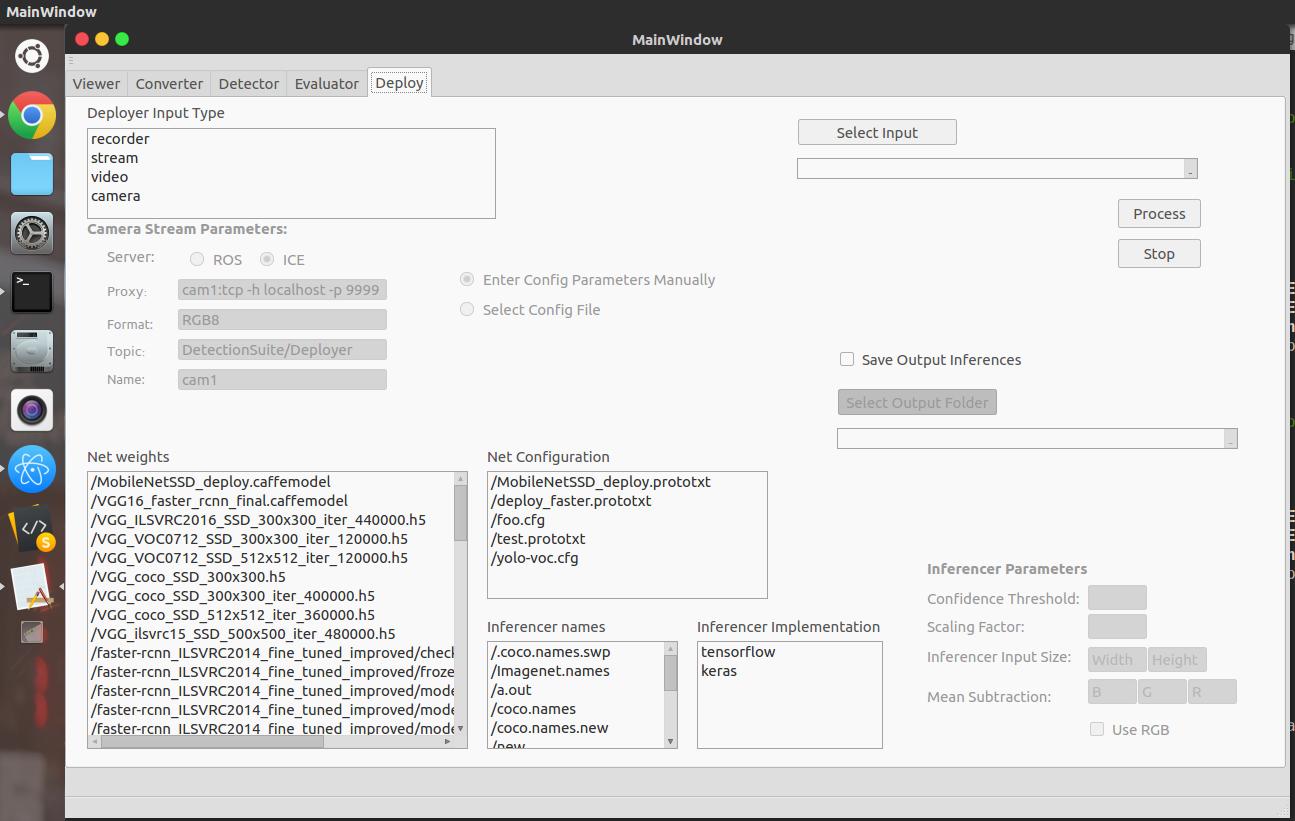
Configuring Parameters:
-
Deployer Implementation: Method to fetch input images, can be
Camera,VideoorStreams. For video, select a video file. For streams, select between ROS or ICE, and enter the config parameters manually or select a config YAML file. -
Net Weights: Select weights, for the inferencer to be used.
-
Net Config: Select Config file for the corresponding inferencer.
-
Inferencer Implementation: Can be Tensorflow, Keras, Caffe, PyTorch or Darknet.
-
Inferencer Names: Dataset classNames using which the inferencer was trained.
-
Save Inferenced Samples (optional): If you require to save inferenced images with bounding box detections or masks, class ids and confidence scores, then check it and select the output folder.
-
Inferencer Params (For Caffe Only): Parameters specific to inferencer. Some sample parameters for the same are listed on our model zoo.