Color Filter
Goal
In this practice the intention is to develop a color filter that allow us to segment some object in the image. You will have to get in contact with RGB and HSV color spaces, and OpenCV (Python) library.
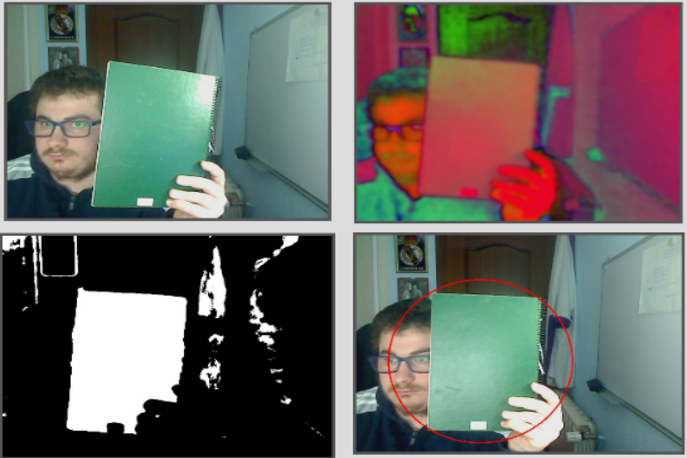

Instructions
This is the preferred way for running the exercise.
Installation
- Clone the Robotics Academy repository on your local machine
git clone https://github.com/JdeRobot/RoboticsAcademy
-
Download Docker. Windows users should choose WSL 2 backend Docker installation if possible, as it has better performance than Hyper-V.
-
Pull the current distribution of Robotics Academy Docker Image
docker pull jderobot/robotics-academy:latest
How to perform the exercise?
- Start a new docker container of the image and keep it running in the background. It is necessary to map the port where the camera is located to the docker container.
- For ubuntu: The port to map will be in /dev/videoX , you should check the number where your camera is connected. For example /dev/video0
docker run --rm -it -p 7164:7164 -p 2303:2303 -p 1905:1905 -p 8765:8765 -p 6080:6080 -p 1108:1108 --device /dev/video0:/dev/video0 jderobot/robotics-academy
-
For MacOs and Windows: A number of configurations must be made in order to map the ports. You can visit this documentation for it.
-
On the local machine navigate to 127.0.0.1:7164/ in the browser and choose the desired exercise.
-
Wait for the Connect button to turn green and display “Connected”. Click on the “Launch” button and wait for some time until an alert appears with the message
Connection Establishedand button displays “Ready”. -
The exercise can be used after the alert.
Where to insert the code?
In the launched webpage, type your code in the text editor,
from GUI import GUI
from HAL import HAL
# Enter sequential code!
while True:
# Enter iterative code!
Using the Interface
-
Control Buttons: The control buttons enable the control of the interface. Play button sends the code written by User to the Image. Stop button stops the code that is currently running on the Image. Save button saves the code on the local machine. Load button loads the code from the local machine. Reset button resets the simulation (primarily, the image of the camera).
-
Brain and GUI Frequency: This input shows the running frequency of the iterative part of the code (under the
while True:). A smaller value implies the code runs less number of times. A higher value implies the code runs a large number of times. The numerator is the one set as the Measured Frequency who is the one measured by the computer (a frequency of execution the computer is able to maintain despite the commanded one) and the input (denominator) is the Target Frequency which is the desired frequency by the student. The student should adjust the Target Frequency according to the Measured Frequency. -
RTF (Real Time Factor): The RTF defines how much real time passes with each step of simulation time. A RTF of 1 implies that simulation time is passing at the same speed as real time. The lower the value the slower the simulation will run, which will vary depending on the computer.
-
Pseudo Console: This shows the error messages related to the student’s code that is sent. In order to print certain debugging information on this console. The student is provided with
console.print()similar toprint()command in the Python Interpreter.
Robot API
from HAL import HAL- to import the HAL library class. This class contains the functions that receives information from the webcam.from GUI import GUI- to import the GUI (Graphical User Interface) library class. This class contains the functions used to view the debugging information, like image widgets.HAL.getImage()- to get the imageGUI.showImage()- allows you to view a debug image or with relevant information
Videos
Application Programming Interface
camera.getImage()- to get the image received from servercamera.setColorImage(input_image)- to set color imagecamera.getColorImage()- to get the color imagecamera.setThresholdImage(bk_image)- to set Threshold imagecamera.getDetectImage()- to get the Thresold imagesetDetectImage()- to set the final detected(processed) imagegetDetectImage()- to get the detected image
def execute(self):
# Add your code here
input_image = self.camera.getImage()
if input_image is not None:
self.camera.setColorImage(input_image)
Theory
This exercise is focused on implementing color filter and tracking a color coded object of choice.
Color Space
Color spaces are a way to represent the color channels present in the image that gives the image that particular hue. There are several different color spaces and each has its own significance. Some of the popular color spaces are RGB (Red, Green, Blue), CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Black), HSV (Hue, Saturation, Value), etc. In the figure below, a)RGB Color Space and b) HSV color space can be visualized.
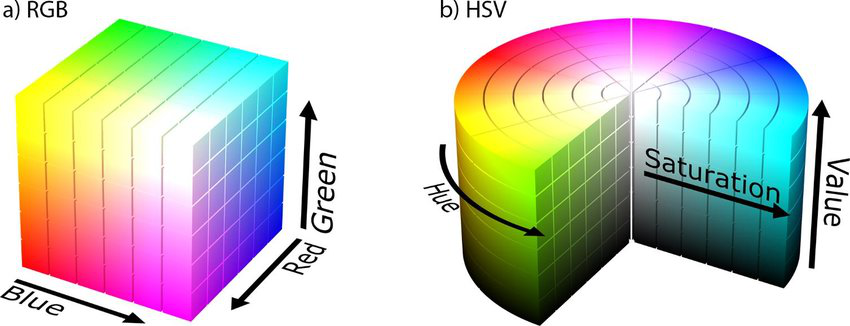
BGR color space: OpenCV’s default color space is RGB. However, it actually stores color in the BGR format. It is an additive color model where the different intensities of Blue, Green and Red give different shades of color. It turns out that this will not work effectively since the RGB values are highly sensitive to illumination making them not great for color detection.
HSV color space: HSV(H : Hue represents dominant wavelength S : Saturation represents shades of color V : Value represents Intensity) stores color information in a cylindrical representation of RGB color points. In HSV, each “tint” of colour is assigned a particular number (the Hue). The “amount” of colour is assigned another number (the Saturation) and the brightness of the colour is assigned another number (the Intensity or Value. It attempts to depict the colors as perceived by the human eye. Hue value varies from 0-179, Saturation value varies from 0-255 and Value value varies from 0-255.
- Hue : This channel encodes color color information. Hue can be thought of an angle where 0 degree corresponds to the red color, 120 degrees corresponds to the green color, and 240 degrees corresponds to the blue color.
- Saturation : This channel encodes the intensity/purity of color. For example, pink is less saturated than red.
- Value : This channel encodes the brightness of color. Shading and gloss components of an image appear in this channel.
It is mostly used for color segmentation purpose and for identifying contrast in images. These color spaces are frequently used in color selection tools in software and for web design. HSV is widely used for building color filters due to its good invariability to illumination.
CMYK color space: Unlike, RGB it is a subtractive color space. The CMYK(cyan, magenta, yellow, and key (black)) model works by partially or entirely masking colors on a lighter, usually white, background. The ink reduces the light that would otherwise be reflected. Such a model is called subtractive because inks “subtract” the colors red, green and blue from white light. White light minus red leaves cyan, white light minus green leaves magenta, and white light minus blue leaves yellow.
In reality, color is a continuous phenomenon, meaning that there are an infinite number of colors. Color spaces, however, represent color through discrete structures (a fixed number of whole number integer values), which is acceptable since the human eye and perception are also limited. Color spaces are fully able to represent all the colors we are able to distinguish between.
Hints
Simple thresholding, Adaptive thresholding, Otsu’s thresholding
Contributors
- Contributors: Carlos Awadallah, Naman Jain, Jose María Cañas, Nacho Arranz, Nemath Ahmed, Vanessa Fernández, Jessica Fernández, David Valladares
- Maintained by Nemath Ahmed
References
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/color-spaces-in-opencv-python/
- https://www.learnopencv.com/invisibility-cloak-using-color-detection-and-segmentation-with-opencv/
- https://www.learnopencv.com/color-spaces-in-opencv-cpp-python/
- https://opencv-python-tutroals.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python-visualizing-image-in-different-color-spaces/?ref=rp
- https://realpython.com/python-opencv-color-spaces/
- https://medium.com/@jijupax/connect-the-webcam-to-docker-on-mac-or-windows-51d894c44468